In the realm of LED displays, two prominent technologies stand out: Chip On Board (COB) and Surface Mounted Device (SMD). Both technologies have revolutionized the digital signage and lighting industries but in distinctly different ways. This blog post delves into the core differences between COB and SMD LEDs, exploring their construction, performance, applications, and suitability for various environments.
Technology and Construction
COB (Chip On Board) technology involves mounting multiple LED chips directly on a substrate to create one module. These chips are packaged together under a single phosphor layer which acts as a diffuser. This method results in a panel where the light emitting diodes are less distinguishable and appear as a continuous light-emitting surface.
SMD (Surface Mounted Device) LEDs, on the other hand, consist of individual LEDs that are mounted onto a circuit board. Each LED in an SMD panel is a distinct unit that combines red, green, and blue diodes, which can be clearly seen as separate components. This allows for precise control over color blending and intensity, making SMD technology prevalent in situations where color accuracy and control are crucial.
Resolution and Pixel Pitch
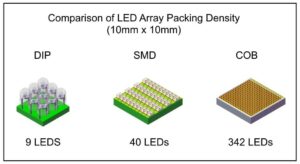 One of the most significant differences between COB and SMD technology lies in their capability for resolution. COB LEDs can support a much smaller pixel pitch because of their ability to place LED chips closer together. This capability makes COB ideal for high-resolution screens that are viewed from short distances.
One of the most significant differences between COB and SMD technology lies in their capability for resolution. COB LEDs can support a much smaller pixel pitch because of their ability to place LED chips closer together. This capability makes COB ideal for high-resolution screens that are viewed from short distances.
SMD LEDs typically have a larger pixel pitch, which was initially a limitation for achieving ultra-high resolutions. However, advances in technology have seen the development of SMD LEDs with smaller pixel pitches, though these solutions can be more expensive than their COB counterparts when achieving comparable resolutions.
Durability and Reliability
Durability is another area where COB technology excels. The encapsulation of LED chips in COB LEDs protects them from many environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical impact. This robust protection makes COB LEDs particularly suitable for outdoor or industrial applications where conditions can be harsh.
SMD LEDs, while also reliable, are more vulnerable to damage because each diode sits exposed on the circuit board. However, they are generally easier to repair or replace due to their modular design, whereas damage to a COB module might require the replacement of the entire unit.
Heat Dissipation
Heat management is crucial for the longevity of LED displays. COB LEDs generally have better heat dissipation capabilities because the LED chips are more densely integrated and spread heat across a larger surface area on the substrate. This efficient heat dissipation contributes to the longevity and color stability of COB LEDs.
In contrast, each SMD LED generates heat independently and must dissipate it without affecting neighboring diodes. This can make heat management more challenging, especially in larger or denser SMD setups.
Light Quality and Viewing Experience
 The diffused nature of COB LEDs provides a more uniform light output which can be easier on the eyes, making it ideal for applications where viewers may be close to the screen, such as in indoor advertising or information displays.
The diffused nature of COB LEDs provides a more uniform light output which can be easier on the eyes, making it ideal for applications where viewers may be close to the screen, such as in indoor advertising or information displays.
SMD LEDs offer superior control over color blending and intensity, allowing for vivid, high-contrast images that are essential in situations where visual impact is key, such as in broadcasting or dynamic outdoor advertising.
Cost Considerations
Generally, COB LEDs can be more cost-effective in high-resolution applications because they use fewer components per pixel. However, the initial cost and the complexity of manufacturing COB LED displays might be higher than SMD.
SMD LEDs are more standardized and widely used, which often makes them less expensive in general applications and easier to replace or upgrade.
Applications
Due to their robustness and excellent color uniformity, COB LEDs are increasingly used in environments where fine detail is crucial, such as in museums, galleries, and intricate designs or where the display will be subject to rough conditions.
SMD LEDs are prevalent in general lighting, large format outdoor displays, and situations where bright, colorful presentations are required. They dominate in consumer electronics, automotive lighting, and large-scale commercial displays.
Conclusion
Choosing between COB and SMD LED technologies depends heavily on the specific needs of the project, considering factors such as viewing distance, environmental conditions, desired image quality, and budget. COB LEDs offer advancements in durability and resolution, making them suitable for high-end, close-range applications, while SMD LEDs continue to provide versatility and vibrant color performance for general and diverse uses.
As technology progresses, the gap between these two technologies may narrow, but for now, understanding their distinct advantages is crucial for making informed decisions in the rapidly evolving LED market.



